斐波那契数列指以 0、1、1、2、3、5、8... 之后每一项都是前面两项数字之和这种规律排列的数组。给定 n,计算数列第 n 项的值。
后续提问方向:
输入两个有序的链表的头节点,返回合并好的链表的头节点。如输入 1->2->4 和 1->3->4,输出 1->1->2->3->4->4
后续提问方向:
输入一个链表的头节点,输出该链表反转后的头节点。如输入 1->2->3,输出 3->2->1
后续提问方向:
给定由 '('、')'、两种字符的字符串,验证左右括号是否配对。
- ")(()))" => false
- "(())((()())())" => true
后续提问方向:
- 困难-增加星号字符,"*",可作为单个左括号或单个右括号或空字符串使用,测试用例“(((((())*)))()))(()((*()*(*)))(*)()”
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。
后续提问方向:
给定二叉树的根节点 root,返回树的层序遍历的结果。
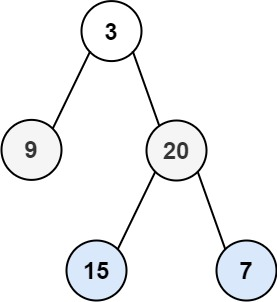
输入:如上图所示。输出:[[3],9,20,15,7]
用例
const a = {
name: 'a',
say() {
console.log(this.name)
},
}
const c = {
name: 'c',
}
a.say.bind(c)() // "c"
参考实现
Function.prototype.bind = function bind(context = globalThis) {
const fn = this
context.fn = fn
return (...args) => {
const res = context.fn(...args)
delete context.fn
return res
}
}
instanceof 运算符先通过检测类的 Symbol.hasInstance 来判断对象是否是类实例,如果没有相应方法则检测构造器的原型在不在对象的原型链上。
参考实现
function _instanceof (val, fn) {
const hasInstance = fn[Symbol.hasInstance]
if (hasInstance) {
return fn[Symbol.hasInstance](val)
}
const proto = fn.prototype
while ((val = Object.getPrototypeOf(val))) {
if (val === proto) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
后续提问方向:
- 困难-有哪些判断类型的方法?各有什么优缺点?
- 偏门-创造一个类 God 使得
null instanceof God 为真
参考实现
function cloneDeep (obj) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
return obj
}
if (obj instanceof Array) {
return obj.map(cloneDeep)
}
return Object.entries(obj).reduce((h, [k, v]) => {
h[k] = cloneDeep(v)
return h
}, {})
}
后续提问方向:
- 中等-如何支持多种类型,如 Function、Symbol、Undefined、RegExp、Math
- 中等-如何处理对象间循环引用
用例
const add = curry(function (a, b) { return a + b })
const add5 = add(5)
add5(6) // 11
参考实现
const curry = (fn, ...args) => {
if (args.length >= fn.length) {
return fn.apply(null, args)
} else {
const newFn = (...extraArgs) => curry(fn, ...args, ...extraArgs)
Object.defineProperty(newFn, 'length', { value: fn.length - args.length })
return newFn
}
}
用例
// 输入
[
{
id: "1",
name: "page",
},
{
name: "page-name",
id: "2",
parent: "1",
},
{
name: "text",
id: "3",
parent: "2",
},
{
name: "text",
id: "4",
parent: "2",
}
]
// 输出
[
{
"id": "1",
"name": "page",
"components": [
{
"name": "page-name",
"id": "2",
"parent": "1",
"components": [
{
"name": "text",
"id": "3",
"parent": "2",
},
{
"name": "text",
"id": "4",
"parent": "2",
}
]
}
]
}
]
参考实现
function toTree (data) {
data = data || []
const map = {}
const roots = []
data.map(x => map[x.id] = x)
data.map(x => {
if (map[x.parent]) {
map[x.parent].components = map[x.parent].components || []
map[x.parent].components.push(x)
} else {
roots.push(x)
}
})
return roots
}
用例
const fileNames = ["1.txt", Promise.resolve("2.txt"), "3.txt"]
Promise.mapSeries(fileNames, function(fileName, index, arrayLength) {
return fs.readFileAsync(fileName).then(function() {
return fileName + "!"
});
}).then(function(result) {
console.log(result)
// ["1.txt!", "2.txt!", "3.txt!"]
})
参考实现
Promise.mapSeries = (arr, fn) => {
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
throw new TypeError(`Promise.mapSeries requires array, but got ${typeof arr}`)
}
return new Promise(async (resolve) => {
const results = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const val = await Promise.resolve(arr[i])
results[i] = await fn(val, i, arr.length)
}
resolve(results)
})
}
后续提问方向:
参考实现
[...new Set([...document.querySelectorAll('*')].map(x => x.tagName))]
// ['HTML', 'DIV', 'SPAN', ...]
设计一个支持扩展的排序函数。使得给定的食物列表按照价格升序、评分降序的顺序排列。
用例
const food = [
{ name: "Suger", price: 1, rating: 3 },
{ name: "Chocolate", price: 3, rating: 4 },
{ name: "Burger", price: 3, rating: 2 },
{ name: "Cola", price: 1, rating: 5 },
{ name: "Pizza", price: 5, rating: 3 },
]
food.sort(yourSortFunction)
// [{"name": "Cola","price": 1,"rating": 5},
// {"name": "Suger","price": 1,"rating": 3},
// {"name": "Chocolate","price": 3,"rating": 4},
// {"name": "Burger","price": 3,"rating": 2},
// {"name": "Pizza","price": 5,"rating": 3}]
参考实现
const sort = map => compareFn => (a, b) => compareFn(map(a), map(b))
const flipComparison = fn => (a, b) => -fn(a, b)
const byValue = (a, b) => a - b
const byPrice = sort(e => e.price)(byValue)
const byRating = sort(e => e.rating)(flipComparison(byValue))
const sortFlattend = sortFns => (a, b) => sortFns.reduce((sortResult, fn) => sortResult || fn(a,b), 0)
const byPriceThenRating = sortFlattend([byPrice, byRating])
// food.sort(byPriceThenRating)
function recur(n) {
if (n === 0) console.log(n)
else recur(n - 1)
}
recur(500000)
// >>> RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
- 简单-将该函数转换为循环的写法避免栈溢出
- 困难-使用任意循环以外的方法改写函数避免栈溢出
参考实现
function recur(n) {
if (n === 0) console.log(n)
else return () => recur(n - 1)
}
function trampoline(fn) {
let res = () => fn()
while (res instanceof Function) {
res = res()
}
return res
}
trampoline(recur(50000000)) // 0
任意技术栈。给定商品的规格信息以及库存列表,实现商品的全排列表格。表格行首有 checkbox,表格能多选,但如果库存中没有此行的商品规格则此行不能被选中。
基础代码及用例
 代码地址:Element Plus Playground
代码地址:Element Plus Playground
用例
interface Todo {
title: string
description: string
completed: boolean
}
type TodoPreview = MyOmit<Todo, 'description' | 'title'>
const todo: TodoPreview = {
completed: false,
}
参考实现
type MyOmit<T, K extends keyof T> = {
[P in Exclude<keyof T, K>]: T[P]
}
用例
// trimed expected to be 'Hello World'
type trimed = Trim<' Hello World '>
参考实现
type Trim<S extends string> = S extends
| `${' ' | '\t' | '\n'}${infer Rest}`
| `${infer Rest}${' ' | '\t' | '\n'}`
? Trim<Rest>
: S
用例
type X = {
x: {
a: 1
b: 'hi'
}
y: 'hey'
}
type Expected = {
readonly x: {
readonly a: 1
readonly b: 'hi'
}
readonly y: 'hey'
}
type Todo = DeepReadonly<X> // should be same as `Expected`
参考实现
type DeepReadonly<T extends any> = {
readonly [P in keyof T]: T[P] extends (...args: any[]) => any
? T[P]
: DeepReadonly<T[P]>
}

 代码地址:
代码地址: